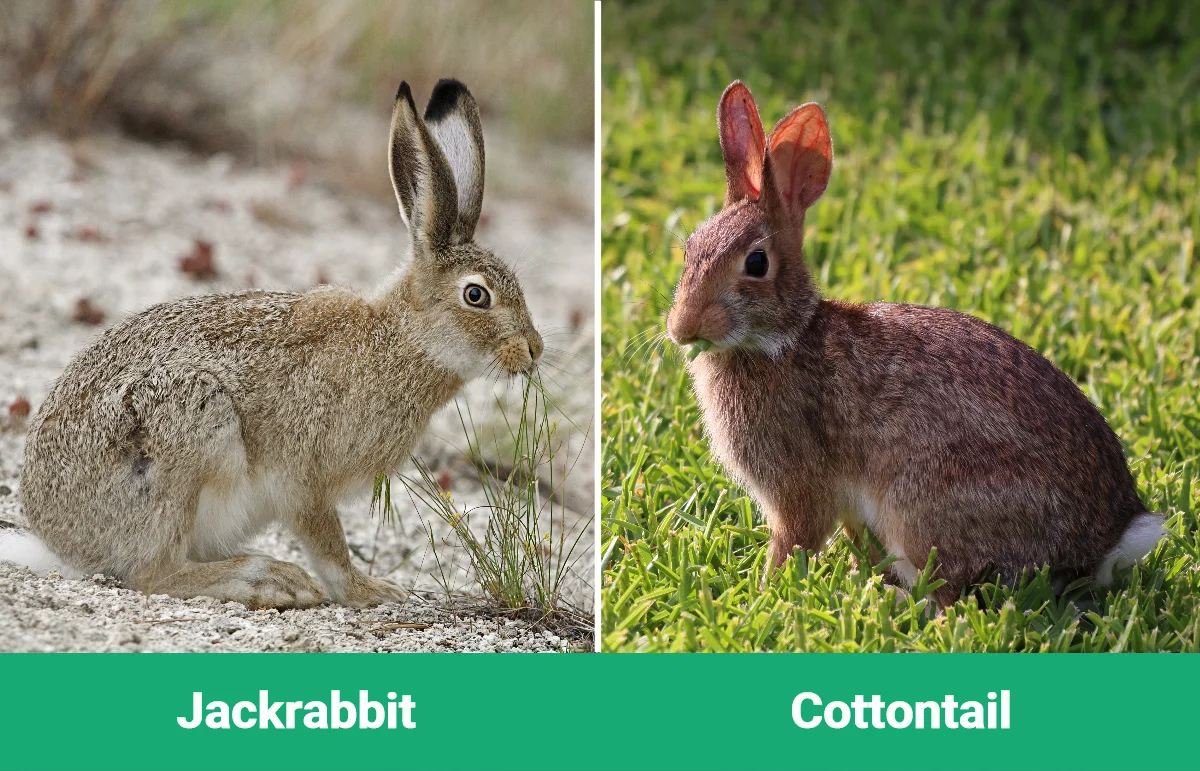
If you are from the western United States, you have probably seen or at least heard of the Jackrabbit, as they are native to that region. You can also find them in Mexico. The Cottontail rabbit is found all over the United States and Central and South America. Both belong to the same family, Leporidae. However, there are several differences between them that we will look at here, along with their similarities.
Visual Differences
At a Glance
- Average height (adult): 24 inches
- Average weight (adult): 3–6 pounds
- Lifespan: 5 years
- Distribution: The Western United States and Mexico
- Diet: Shrubs, small trees, grasses, and forbs
- Predators: Hawks, eagles, coyotes, bobcats, lynxes, dogs, cats, owls, foxes
- Average height (adult): 15–18 inches
- Average weight (adult): 1–2 pounds
- Lifespan: 2 years
- Distribution: North, Central, and South America
- Diet: 145 different plants, stems, branches, seeds
- Predators: Hawks, cats, snakes, dogs, coyotes, owls, opossums, badgers, squirrels

Jackrabbit Overview
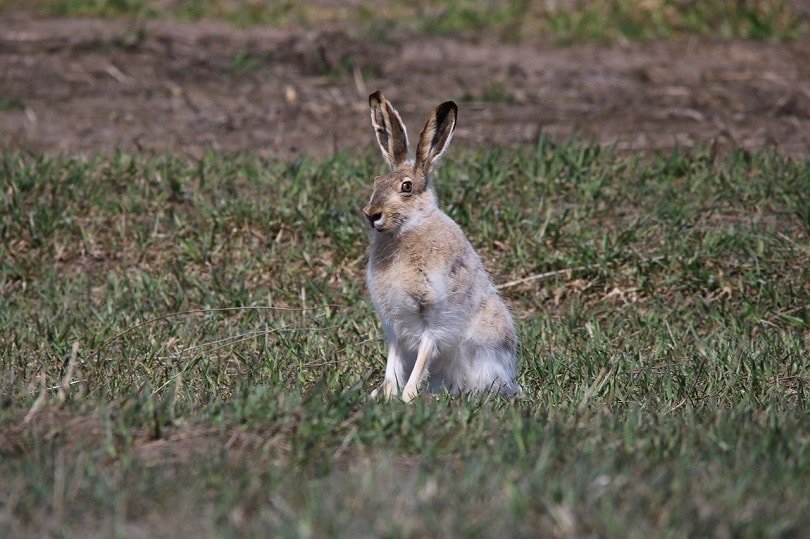

Jackrabbits are not rabbits at all but hares. They have long and powerful back legs capable of speeds up to 45 miles per hour and long ears. Their name is a shortened version of their original name, Jackass Rabbits, which they got because of their ears, as they are long and donkey-like. There are three kinds of Jackrabbits: the Antelope Jackrabbit, the White-Tailed Jackrabbit, and the Black-Tailed Jackrabbit. Many people consider the Alaskan Hare to be the fourth type.
Health & Care
Jackrabbits can adapt to several different habitats, as long as there are many types of plants in the area. This animal requires various grasses, shrubs, and flowers to get the nutrients that they need. They also prefer open areas with tall grasses and sparse coniferous trees to closed forests, so they have room to run. Shrubs are perfect places to hide during the day, and tall grasses provide food at night.
Breeding
Female Jackrabbits begin to breed in the spring of their second year or after reaching 7 months of maturity. The breeding season varies by location, and northern Jackrabbits will breed from February to May. In southern states, the breeding season can start as early as January and stretch until July. More litters are born in warm climates, while litter sizes are larger in the northern states.
Jackrabbits give birth above ground in a hastily created nest that may or may not be lined with fur. The young are born with open eyes and fur and will begin hopping almost immediately. Females do not protect or stay with the young after a few weeks.
Cottontail Overview
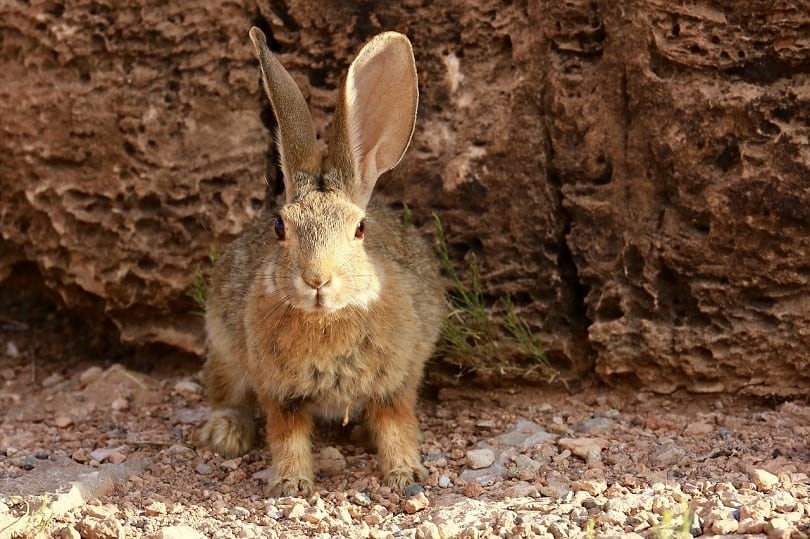

The Cottontail rabbit is much smaller than a hare and has a short tail with white fur on the underside that gives this animal their name and unique look. They usually only live about 2 years, mainly because almost every carnivorous animal, including squirrels, likes having them for dinner. You can find Cottontail rabbits practically anywhere in the United States and Central and South America. They even survived being introduced to British Columbia, Canada.
- Related Read: Mountain Cottontail
Health & Care
Unlike most rodents, which use their front paws as hands while they eat, Cottontail rabbits eat on all fours and use their nose to move their food around. However, they may use their paws to bring food on low-lying branches into reach. They usually eat many of the same grasses, seeds, twigs, bark, and herbs that a Jackrabbit eats.
Rabbits are social animals but build underground burrows that they like to stay in, especially on windy days because the wind can affect their hearing.
Breeding
Cottontail rabbits can give birth as often as every 3 weeks, producing four to six offspring each time. The female Cottontail rabbit will dig a shallow nest covered with fur and grass to hide the newborns when they arrive. Baby Cottontails are hairless and cannot see but will be ready to leave the nest in about 3 weeks, when the mother is ready to give birth again. The mother can begin mating again just a few hours after giving birth.

Summary
Both the Jackrabbit and the Cottontail rabbit have many predators. The Jackrabbit has a few more tricks to get away, like the ability to achieve high speeds. However, they prefer to stay out in the open where they can see predators like hawks. Conversely, the Cottontail rabbit likes to hide under low-lying conifers and underground burrows. Unfortunately, due to their slow speed and wide distribution area, predators often catch this rabbit, and they are one of the primary sources of food for many animals, including house cats. You can attract Cottontails to your yard with plenty of thick vegetation and conifer trees, but if you have ever tried to grow a garden, you know that these animals can also be a nuisance.
We hope that you have enjoyed reading over this comparison and have learned the difference between these two related but very different species!
Featured Image Credit: Top – blazejosh, Pixabay | Bottom – Vincent Pro Photo, Shutterstock
