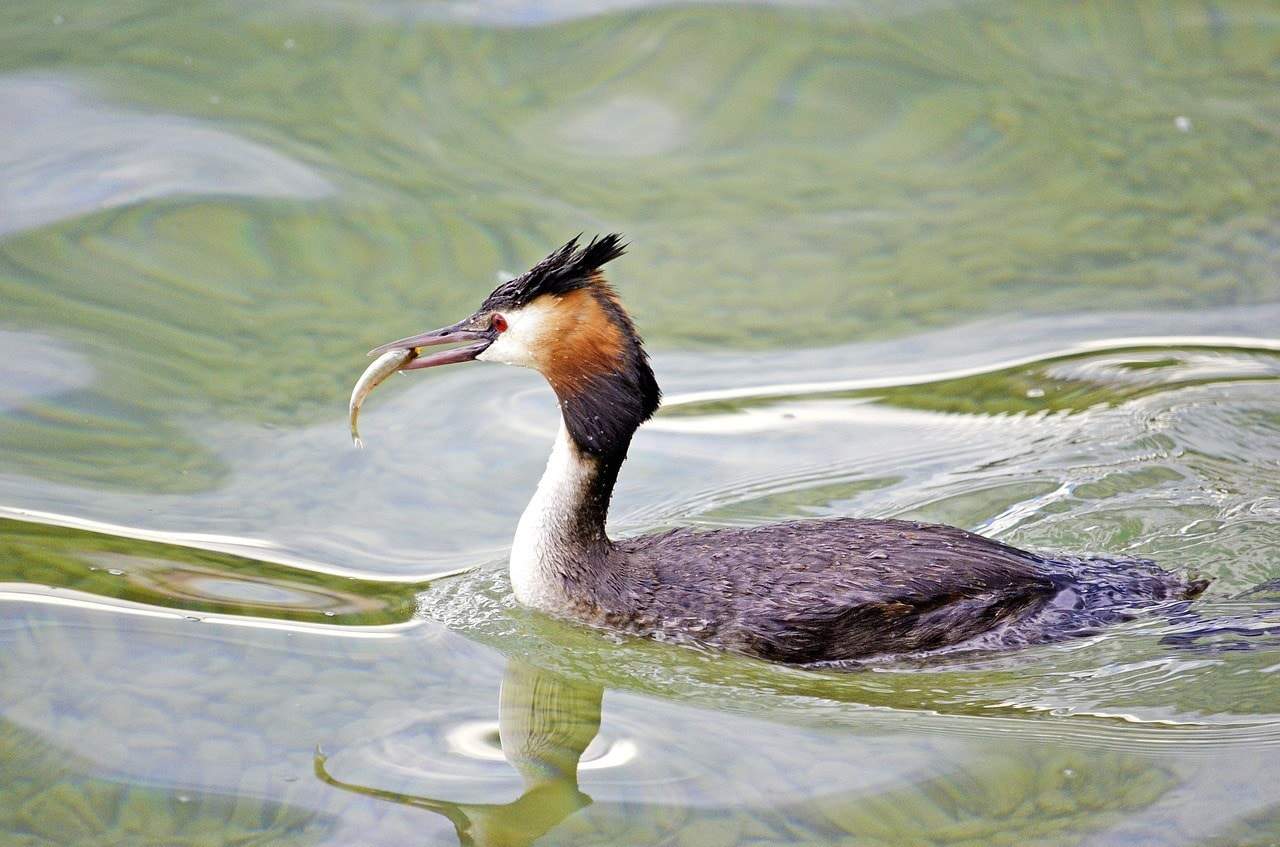
We’ve all seen ducks eating while swimming in a pond or other bodies of water. But have you ever wondered what they are actually eating? Many aquatic bird species eat fish as a staple diet, but what about ducks? Do ducks eat fish?
Ducks eat a wide variety of food that fits their nutritional needs, and yes, ducks do eat fish. But the kind of fish depends on the species of the duck.
Here, we look at not only the kind of fish that ducks eat but what else makes up their regular diet. We also look at how ducks eat, including interesting information about their bills.
A Little Bit About Ducks
Ducks are a part of the Anseriformes family, which includes geese and swans, and there are as many as 162 species around the world. Out of all of these species, you might be surprised to learn that there are only two that are among the domestic duck breeds: the Muscovy and the Mallard. All domestic ducks have descended from one of these species (but especially the Mallard).
They are social birds that feel more comfortable when with a larger group of birds. Since they spend so much time around bodies of water, they are also known as “waterfowls.”

The average lifespan for ducks is typically 5 to 10 years. That said, ducks can live for up to 20 years if they are well cared for. The world record for longest living duck goes to a pair of ducks from South Africa that lived until they were 49!
If you’ve ever heard the saying, “water off a duck’s back,” it essentially means not letting insults or criticisms bother you. This came about because ducks have waterproof feathers, and water literally rolls off the duck’s feathers. When they dive down to feed, even the soft downy feathers next to their skin stay entirely dry.
What Do Ducks Eat?
Ducks are omnivores and foragers. They eat a variety of vegetation and animal matter, and they search widely for the best food. What ducks eat depends on the species and their age.
Generally speaking, ducks will eat:
- Small fish
- Fish eggs
- Aquatic plants and algae
- Seeds and grain
- Weeds
- Grass
- Salamanders
- Frogs and tadpoles
- Insects and larvae
- Roots

A Little Bit About the Duck’s Bill
Ducks have beaks, or bills, that help them catch and swallow their food. Ducks are either diving (to find their food) or dabbling (feeding on the surface of the water).
Dabbling ducks have bills that are soft around the edges because they find their food through touch, so their bills enable them to feel for their food. They also have a small nail at the end of their bills that is used to snag and manipulate their food.
Waterfowl bills also have something called lamellae, which are tiny notches found just inside their beaks and look a bit like teeth. These structures act like sieves, enabling the ducks to sift and expel anything that they don’t want to eat, like water and mud. The lamellae also enable waterfowl to get a good grip on slippery food, like fish.
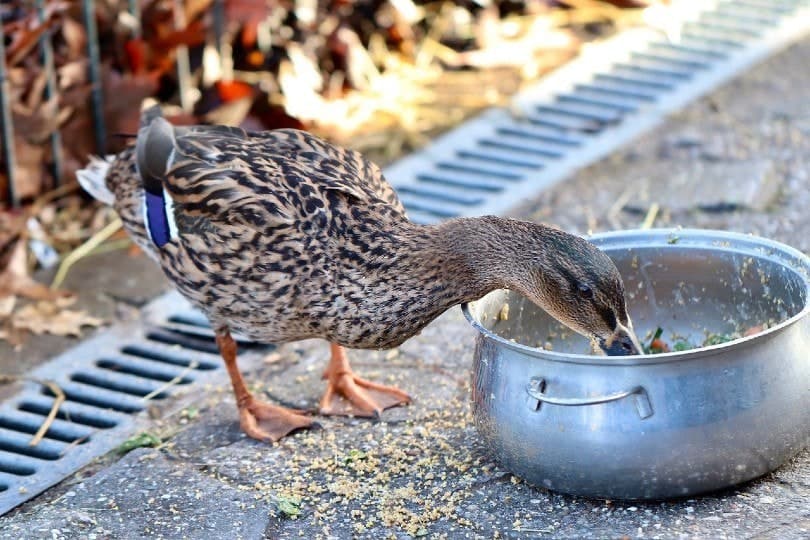

A Little Bit About How Ducks Eat
How ducks eat and digest their food is quite interesting. Since ducks don’t have teeth, they swallow their food whole. The food enters their gizzard, which is a muscular organ found in their stomach, and is ground up there so it can be easily digested.
Some duck species, like the Scaup and Eider, can actually swallow clams and mussels whole, shell and all, and their gizzards will grind it all up for them.
Ducks will also deliberately eat small stones and sand, which are then stored in the gizzard to assist in the grinding process.

Let’s Talk About Those Fish
The kind of fish that a duck eats depends on the species and the size of the duck. Small ducks eat small fish, and large ducks eat large fish.
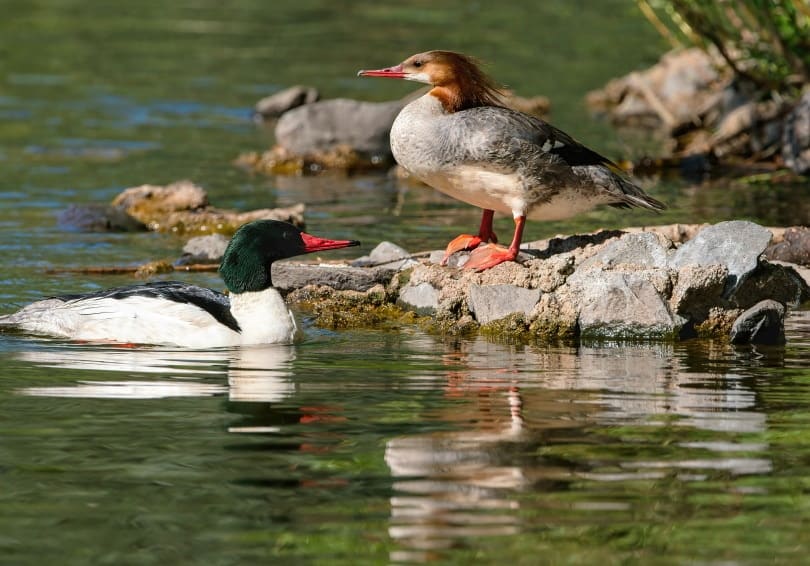
That said, only one species of duck eats fish as a predominant part of their diet: the Common Merganser.
Common Merganser
These ducks eat mainly fish, as well as mollusks, worms, crustaceans, frogs, plants, birds, and insects.
During the winter months, they eat primarily fish, which include:

- Trout
- Salmon
- Shad
- Sticklebacks
- Suckers
- Minnows
- Chub
- Sunfish
- Eels
Other Ducks
Mallards eat a wide variety of food, such as seeds, aquatic vegetation, earthworms, aquatic insect larvae, freshwater shrimp, snails, and grain. They do eat fish, but these aren’t as much of a staple in their diets as they are for the Merganser. Mallards tend to eat much smaller fish, such as minnows, guppies, and graylings.
This also goes for most other duck species. Since they are foragers, they feed on what is in reach, but you can expect diving ducks to go after large species of fish.

If You Have a Pond
If you have a pond and keep fish, you can probably expect geese and ducks to find their way there eventually. If you keep small fish among the usual aquatic plants, almost any kind of duck would be happy to call it home.
However, large fish aren’t eaten as frequently. Large Koi, for example, aren’t necessarily gobbled up by most ducks, but you’ll still have to look out for cats, herons, raccoons, dogs, hawks, owls, snakes, and egrets — and possibly the Merganser!

Conclusion
Ducks do eat fish among a variety of other food sources. Fish provides humans with various health benefits, and the same can be said for ducks. Rich in omega-3 fatty acids but low in fat and high in protein, fish can make a duck’s diet a healthy one. It provides them with long-lasting energy too.
Diving ducks tend to eat more fish than dabbling ducks because they dive into deeper waters and are more capable of chasing fish down (the Merganser is a diving duck). So, while most ducks aren’t heavy fish eaters, they will eat them if they’re the right size and the opportunity presents itself.
- Related read: Do Ducks Have Teeth?
Featured Image Credit: Pixabay
